|
LESSON 4 : VEDIC
METHOD OF INSTRUCTION : (PART - 1)
|
|
|
| |
| Ancient Indian teaching methods involved a
personal instruction by the teacher to his disciple.The teacher, called as ''Guru',
would generally live in seclusion, away from city life, and have a select group
of disciples, called 'Shishyas'. It would only be the good fortune of a
'shishya' if he managed to secure a good 'guru'. Similarly, a great 'guru'
would strive to find a deserving disciple. The teacher-disciple relation used
to be a highly affectionate relationship, with the teacher commanding the same,
nay more, reverence from his disciple as the latter owed to their parents. The
ancient historical records of India find their place in the Puranas.
In these Puranas, generally there is a story being told by an elevated sage to
one or more seekers of knowledge.
|
| |
| The
Signs |
| There are twelve signs of the zodiac. One of
the signs happens to be the sign rising at the eastern horizon at the time of
birth. This rising sign is called the lagna or the ascendant. The lagna
happens to be the first house of the horoscope.By this is meant that the houses
and signs do not coincide. The first house has the label of the sign rising at
the time of birth, the second bears the label of the sign that will rise next,
and so on. |
| The nine grahas (from the Sun to Ketu) or
'planets' are the occupants of these houses. The houses represent certain
characteristics.The signs falling in these houses also represent certain
characteristics, and the two intrmingle to indicate something newer.Then the
planets which occupy them inflict further modifications. |
| In order to be able to make any fruitful
predictions, it is essential to understand the meanings of the signs, houses
and planets. |
| |
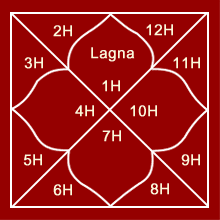
| A Horoscopic Chart |
| (A) North Indian Chart is the one in
which the order of the houses is fixed. It consists of four central rhomboidal
houses (which are numbered 1, 4,7 and 10, starting from the upper central
rhomboid) and eight triangular houses. The sign rising at the time of birth is
marked in the first house or the upper central rhomboid, and the remaining
signs marked in regular order in an anti-clockwise direction. |
|
|
| (B) The South Indian Chart has the signs
in a fixed order in the chart. The lagna is marked in the appropriate sign. The
remaining houses are counted in a clock-wise direction. |
|
|
| (C) An Eastern Indian Chart, often used
in Bengal and Orissa, also has the signs in a fixed order in the chart. The
ascendant is marked in the appropriate sign. The remaining houses are counted
in an anti-clockwise direction.
|
|
|
| Whatever the type of horoscopic chart
preferred, the planets are placed in the houses bearing the signs in which the
planets are located astronomically. |
| |
| The Signs ( or Rashis ) |
| The signs of the zodiac have special features
which are being described here. |
| (1) Appearance
and Habitat : The
twelve signs of the zodiac each have a specific appearance and a habitat.
|
|
The sign Mesha resembles a ram. It
circulates among the goats, the sheep and region holding wealth and precious
stones. It wanders on grassy lands, and around lakes surrounded by vegetation. |
|
The sign Vrisha resembles a bull.
Cowhouses and farmlands are its place of residence. |
|
A man and a woman bearing a trumpet and a harp
represent the sign Mithuna whose places of residence are the couch and
the lounge.This dual sign haunts the sports lovers and the pleasure houses. |
|
Karkata
has the appearance of a crab and lives in water. Its places of residence
include water-filled garden beds,river banks and un-inhabited lands. |
|
Simha (resembling a lion) resides in the
mountains, forests, caves, inaccessible places, deep ditches and the living
places of hunters. |
|
Kanya (consists of a woman) standing in
a boat and holding corn and a lamp in her hand, inhabits women's pleasure
rooms. |
|
Narda! Tula is represented by a man
holding a balance in his hands, and its residences include lanes, bazaars,
towns, routes and buildings. |
|
Vrishchika resembles the scorpion in
appearance. It moves in crevices and pits. Its areas of residence include
poisons, animal excreta, stones and insects. |
|
Of Dhanu, the legs are like those of a
horse. It is radiant and holds a bow and arrow. |
|
The mouth of Makara is like that of a
deer, shoulders like those of a bull and eyes like those of an elephant. It
moves in the rivers and resides in the ocean. |
|
Kumbha resembles a man wearing wet
clothes and holding on his shoulders an empty pitcher.It moves in gambling
houses and resides in drinking dens. |
|
The sign Meena consists of two fishes
lying side by side, the head of one being beside the tail of the other.It
haunts pious places, temples of gods and houses of Brahmins. |
| (2) Parts
of the body :The various
signs from Mesha onwards represent (1) head, (2) face, (3) shoulders, (4)
chest, (5) heart and stomach, (6) abdomen, (7) lower abdomen and groin, (8)
external genitalia, (9) thighs, (10) knees, (11) calves, and (12) feet. |
(3) Stature : Of short stature
are signs Mesha, Vrisha, Kumbha and Meena (i.e., 1, 2, 11 and 12).
Of tall stature are the signs Simha, Kanya, Tula and Vrischika (i.e., 5,
6, 7 and 8).
Of even stature are the signs Mithuna, Karka, Dhanu and Makara (i.e., 3,
4, 9 and 10)
|
|
(4) Diurnal
strength : Strong
during night are the signs
Mesha, Vrisha, Mithuna, Karka, Dhanu and Makara. Except Mithuna, they rise by
the hind side (Prishtodaya)
Strong during day are Simha, Kanya, Tula, Vrischhika, Kumbha and Meena.
Except Meena, they rise by the head(Sheershodaya).
Mithuna too rises by the head.
Meena rises both by the head and the tail (Ubhayodaya)
|
| (5) Malefic/Male
: Odd signs, viz., 1, 3, 5,
7, 9 and 11. |
| (6) Benefic/Female
: Even signs, viz., 2, 4, 6,
8, 10 and 12. |
(7) Movable
or otherwise : Signs 1, 4, 7
and 10 are movable ; they indicate change and mobility. Signs 2,
5, 8 and 11 are fixed ; they indicate stability and fixity.
Signs 3, 6, 9 and 12 are mixed ; they indicate a balance between the
fixed and movable signs.
|
(8)
Directions :
| East |
signs 1, 5 and 9. |
| South |
signs 2, 6 and 10 |
| West |
signs 3, 7 and 11. |
| North |
signs 4, 8 and 12. |
|
(9) Inherent
nature :
| Fiery |
signs 1, 5 and 9. |
| Earthy |
signs 2, 6 and 10 |
| Airy |
signs 3, 7 and 11. |
| Watery |
signs 4, 8 and 12. |
|
(10) Biological
characters :
| Quadrupeds |
signs 1, 2, 5, posterior half of 9, and
anterior half of 10, |
| Bipeds |
signs 3, 6, 7, 11, and anterior half of
9. |
| Insect ( Keeta) |
signs 4 and 8. |
| Those inhabiting water (Jalachara) |
signs 12, and rosterior half of 10. |
|
(11) Constituent
characters :
| Mineral (Dhatu) |
signs 1, 4, 7 and 10. |
| Vegetable (Moola) |
signs 2, 5, 8 and 11. |
| Animal (Jeeva) |
signs 3, 6, 9 and 12. |
|
(12) Caste
:
| Kshatriya |
signs 1, 5 and 9. |
| Vaishya |
signs 2, 6 and 10. |
| Shudra |
signs 3, 7 and 11. |
| Brahmin |
signs 4, 8 and 12 |
|
| (13) Lords
: Of the twelve signs,
starting from Mesha, the lords are respectively Mars, Venus, Mercury, the Moon,
the Sun, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Saturn and Jupiter. |
| |
|
|